FY 2026-27 Annual Compliance Guide Book for Retailers
February 13, 2026

The regulatory landscape in India presents persistent challenges for the retail business, particularly after stores become operational. Retailers need the correct information and know-how to understand the compliance requirements for GST, TDS, and other laws required to run a retail store business in India. They need knowledge about regulatory requirements to comply with national, state, and municipal laws.
Whether you are a small boutique store, a large departmental store, or a supermarket chain, this guidebook will help you to navigate annual compliance requirements for the FY 2026-27.
The operational phase entails continuous adherence to a multitude of compliance requirements stemming from various central, state, and local regulations. Here’s an overview of the complexities faced by the retail industry:
| Year-end compliances ensure that your retail store business stays within the regulatory parameters, and no penalties, fines, or legal action can be taken against you by any authority. |
Retailers must adhere to various financial regulations and reporting requirements to ensure that their operations are in line with the taxation law in India. This includes accurately recording and reporting sales, expenses, and profits, as well as keeping track of inventory and assets. By maintaining proper financial records, retailers can demonstrate transparency and accountability to tax authorities and investors.
Following the policies and laws set using tax government and monetary regulators is called economic and earnings tax compliance. This way, retailers can report financial data and pay taxes as the regulation requires.
How can retailers ensure annual tax compliance?
Critical Components of Financial and Income Tax Annual Compliance:
| Transaction Tracking Maintain information on all sales and charges through receipts and invoices. | Taxable Income Calculation Determine the taxable earnings by deducting allowable expenses from total sales revenue. | Tax Optimization Identify and follow applicable deductions and tax credits unique to shops. |
| Tax Form Preparation Accurately complete all vital tax forms and sales and earnings tax returns. | Tax Filing Submit tax returns and bills to the applicable tax government using the required closing dates. | Financial Review Periodically assesses economic documents to ensure accuracy and compliance with tax regulations. |
Pro Tip: Retailers can rely on robust accounting systems. These systems help retailers track their income and expenses, generate necessary financial reports, and facilitate the preparation of GST returns.
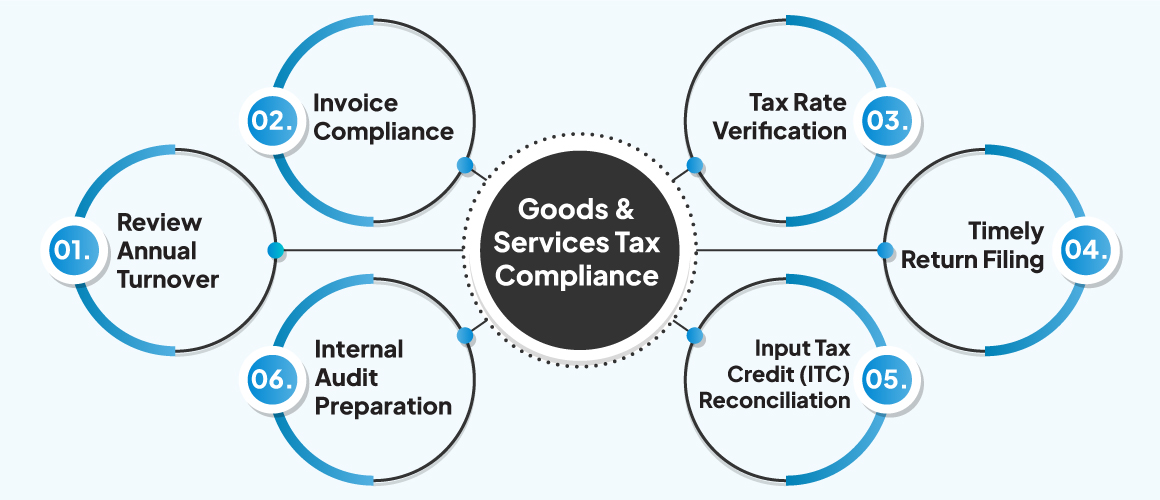
To ensure annual Goods and Services Tax (GST) compliance before the financial year-end, retailers in India must undertake several crucial steps to fulfill their regulatory obligations.
key aspects of annual GST compliance for retailers:
1. Review Annual Turnover: Assess the annual turnover to determine if it exceeds the prescribed threshold for GST registration. Ensure compliance with the threshold for businesses operating within a single state and those operating inter-state.
2. Invoice Compliance: Verify the accuracy and completeness of tax invoices and Bills of Supply issued for taxable sales made to registered and unregistered entities. Ensure that all necessary details, including GSTIN, item description, value, tax rates, and HSN codes, are correctly included in the invoices.
3. Tax Rate Verification: Verify the correct application of GST rates for all products and services to avoid compliance issues. Reconcile the tax rates applied with the prescribed GST rate categories and exemptions.
4. Timely Return Filing: Plan and prepare for the timely filing of various GST returns, including GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and GSTR-9 as per the prescribed filing dates and frequency. Ensure accurate filing to avoid penalties and facilitate the smooth flow of input tax credits.
5. Input Tax Credit (ITC) Reconciliation: Reconcile purchase records with details available on the GST portal to accurately claim and utilize input tax credit. Verify supplier GST compliance and maintain relevant documents such as tax invoices for ITC claims.
6. Internal Audit Preparation: Proactively conduct internal audits to identify and rectify any compliance gaps. Prepare for periodic audits and assessments by the GST authorities by maintaining accurate records and financial data.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) Compliance refers to following regulations of tax deduction and remittance at the source of income. Tax is deducted when the taxpayer makes payments to the payee, after that the deducted amount is transferred to the government on the payee’s behalf.
Retailers are required to deduct TDS on payments made to suppliers, contractors, or service providers if the payment exceeds a certain threshold. This ensures that the government receives its due tax revenue at the time of payment itself.
TDS compliance includes deducting and depositing taxes on diverse bills in line with the Income Tax Act of 1961 provisions.
Critical Aspects of Annual TDS Compliance for Retailers:
| Identification of TDS Applicability Determine whether TDS applies to specific payments or not based on the type of transaction and the thresholds established by tax authorities. | Correct Deduction and Rates Ensure the precise deduction of TDS at the prescribed costs per the Income Tax Act for diverse bills. | Timely Deposit Deposit the deducted TDS amount on the targeted due dates to avoid interest and consequences. |
| Filing TDS Returns File TDS returns appropriately and on time, presenting information of TDS deducted and deposited at some point in the relevant period. | TDS Certificate Issuance Issue TDS certificate to deductees (recipients of income) as proof of TDS deduction, containing info and the quantity deducted and deposited. | Compliance with TDS ProvisionsAdhere to the policies and provisions laid down through the Income Tax Act concerning TDS deduction, deposit, and reporting. |
The Shops and Establishment Act certificate of occupancy is issued by the Municipal Corporation of the city to every retail shop within the city limits as part of the legal registration process.
This certificate imposes specific restrictions and requirements on the retail shop, including:
It is crucial for the Shops and Establishment document to be prominently displayed in the retail store and readily available for inspection by municipal officials during surprise visits to ensure compliance with the specified regulations and standards.
Professional tax is a state-level tax imposed on the income earned by individuals employed in India. Employers are also responsible for deducting and remitting professional tax on behalf of their employees. Retailers, like supermarkets, boutique stores, gift stores, fashion retailers, etc. who employ people on a salary have to pay a fixed amount to the municipal department per employee. The salary should cross a certain threshold for professional tax liability.
For example, in Gujarat PT is deducted at INR 200 per employee whose salary is above INR 12000. (source) Make sure your retail establishment is compliant with PT rules and pay all dues before the month ends in March to avoid any penalties. Retailers also need to file PT returns (both monthly and annual) to avoid action by authorities.
Professional tax compliance also involves adherence to the specific rules and regulations laid down by the respective state governments regarding professional tax, including exemptions, deductions, and penalties for non-compliance. Maintaining accurate records related to professional tax deductions, payments, and filings is essential to demonstrate compliance during audits or inspections by the tax authorities.
For e-retailers, TDS liability may arise in certain cases such as payments made to vendors or service providers for advertising or marketing services. E-retailers need to understand the thresholds and rates at which TDS is applicable and ensure that they deduct and remit the correct amount to avoid any penalties or legal issues.
Critical Aspects of E-commerce Compliance:
| Tax Collected at Source (TCS) E-commerce operators must collect TCS on any substances manufactured through their structures. | GST or goods and service taxes Retailers selling online products have to follow GST regulations for generating invoices, serialization, and remittance. |
| Legal and regulatory standards adherence Retailers need to ensure they follow protocols, and legal statutes and laws governing consumer protection | Transaction validation The accuracy of online transaction details must be verified for validating collected data at the source and GST filings. |
For more details on TDS applicability on e-commerce retailers (e-tailers) read here.
Retail operations generate a significant amount of waste, including packaging materials, expired products, and food waste. Retailers need to have proper waste management systems in place to minimize their environmental impact and comply with hazardous waste management regulations in India. This may involve implementing recycling programs, properly disposing of hazardous materials, and reducing overall waste generation.
Let’s understand how retailers can comply with environmental and municipal regulatory frameworks
Waste management
Pollution control
Compliance with local bodies
| By properly managing waste, controlling pollution, and adhering to local bylaws, retailers can not only meet their legal obligations but also contribute to a healthier environment and a more sustainable community. |
How retailers can ensure environmental and local laws compliance?
Audits are conducted to review and assess a retailer’s financial records and processes to ensure compliance with regulations and standards. Compliance with audit requirements is essential for retailers to demonstrate their commitment to financial transparency and regulatory adherence.
Record-keeping is the most crucial aspect for retailers to ensure annual audit compliance. Retailers must establish and maintain effective record-keeping practices to ensure accurate and complete financial information.
This includes keeping detailed records of:

To comply with audit requirements, retailers must keep records in a systematic and organized manner, using standardized accounting principles, and retail management software that keeps a centralized database of all the above-mentioned types of records. Retailers should also have proper internal controls in place to safeguard their financial records and prevent any unauthorized access or tampering.
Critical aspects of Record-maintaining and Audit Compliance:
| Recordkeeping procedures Set up standard procedures for documentation of financial transactions, data access, cover validation, and storage. For recordkeeping tasks, assign specific roles and responsibilities to a particular person who is accountable and able to maintain consistency. | Maintain detailed financial records Regularly record financial transactions using accounting software with comprehensive details of each transaction, amounts, and their relevant description to support high-quality documentation and maintenance criteria. | Adhere to retention requirements Gain knowledge about tax returns, how to prepare invoices and financial statements, and ensure that records are retained for a specific duration and stored securely or disposed of when no longer required. |
| Organize records effectively Implement a systematic filing system to organize information and classify records by type, date, or department. Use cloud storage solutions or physical filing shelves to collect statistics and facilitate near-term retrieval. | Conducting internal audits Review and perform internal audits of financial facts regularly to identify errors, deviations, or anomalies. Document the audit findings and implement corrective actions to resolve identified issues promptly. | Continuous Improvement Continuously evaluate and improve documentation processes based on audit findings, remarks, and modifications in regulatory requirements. Provide education and assets to employees to improve their file-retaining practices. |
An AGM is a yearly accumulating where shareholders speak, vote, and engage with corporation topics. It is essential to protect transparency, shareholder participation, and desirable governance.
Private limited retailers must call at least one annual General meeting before September 30th of the end of every financial year as per the Indian Companies Act 2013.
Purpose: The AGM is a forum for shareholders to discuss employer issues, vote on critical issues, and engage with authority.
Activities: Engage in discussion of corporate affairs, participate in voting in director elections, and open FAQ sessions.
Procedure: Notification before 21 days should be sent to shareholders. If companies come up with any amendment, the relevant documentation or supplementary material should be provided with the manual.
Compliance: The annual general meeting requirement is essential to maintain stakeholder accountability and foster corporate governance practices.
Employee Provident Fund (EPF) and Employee State Insurance (ESI) compliance are crucial for retailers. Both EPF and ESI compliance are essential to protect employees’ interests and ensure their well-being. Retailers must adhere to these compliance requirements to avoid legal issues and provide a safe and secure work environment for their employees.
EPF is a government-mandated scheme that ensures employees’ financial security by creating a retirement fund. It requires employers to contribute a certain percentage of their employee’s salary to the EPF account.
ESI provides medical and health benefits to employees in case of illness, injury, or maternity.
As a retailer with Private Limited Company status, it is crucial to ensure compliance with the Registrar of Companies (RoC). One of the key requirements is to file annual forms mandated by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), including Form AOC-4 and Form MGT-7, with the RoC.
Form AOC-4 pertains to the submission of financial statements, providing a comprehensive overview of the company’s financial performance during the year. This document is essential for stakeholders, investors, and regulatory authorities to assess the financial health of the company.
Form MGT-7 is the Annual Return that includes details such as the company’s registered office address, directors’ details, shareholding pattern, and other vital information.
ROC updates: You should report to the registrar of companies if any updates in your business operations include hiring new personal adjustments in capital, distribution, or any other facilities that you have provided
By staying compliant with insurance renewals, retailers can have peace of mind knowing that their business is safeguarded against potential financial liabilities.
Retailers must also comply with industry-specific regulations and licenses. It is important for retailers to regularly review their compliance status and take necessary steps to renew or obtain the required licenses and permits. For example, retailers in the food and beverage industry must adhere to the regulations set by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).

Annual compliance holds significant importance for retailers as it ensures legal and financial adherence, thereby contributing to the smooth functioning and reputation of the business. By prioritizing annual compliance, retailers can maintain a strong foundation for sustainable growth and success in the competitive market.
Here are the key points to consider:
Legal Compliance
Tax Obligations
Financial Reporting
Business Credibility
Risk Management
Future Planning
At the end of the guidebook, retailers should prioritize annual compliances to navigate the regulatory maze, uphold legal obligations, mitigate risk, and foster the trust of stakeholders.
Retailers need to manage various compliance requirements during their operational journey, including taxation, licensing, labor laws, and environmental regulations. If you have read the above guidelines, things might be clear in your mind.
If you have any queries, upgrade to VasyERP software compliance requirements and for seamless GST, TDS, and income tax filings. It’s time to say goodbye to manual hassles and ensure government regulations are met effortlessly.

Imagine opening your retail store, only to find your st...
November 29, 2023

The guide to e-invoicing for MSME’s provides the crit...
December 29, 2025
