What is ERP Software? A Complete Guide to ERP Solutions
January 1, 2025

What is ERP Software? ERP systems are key to making retail businesses, industries, and corporate workflows smoother. Without ERP software systems, handling everything from accounting, CRM, inventory and supply chains to procurement, production and distribution will be a mammoth task. What we mean is that manually keeping track of all processes going on in a large-scale retail business or a manufacturing unit is not a practical thing. Businesses that do not deploy unified or central ERP software often depend on disparate systems (individual software systems for each department or activity).
For instance, they implement an inventory management system for their warehouse and stock operations or buy separate accounting software for the finance department. However, this means that each department will have to depend on the other for data and key managers will never get a consolidated view of their business. It will also take time to monitor each software separately.
The solution is ERP software. The real value of ERP lies in its connectedness. It unifies all disparate systems, CRM, inventory management, supplier management, POS, warehouse management, etc. into one system that provides complete end-to-end visibility of your business.
Let us explore its types, key features, and benefits. This article also discusses how businesses can deploy a suitable ERP system for their peculiar business needs.

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software plays a crucial role in helping organizations streamline and merge their key operations. The annual growth rate for ERP software in India is projected at 9.71% CAGR for the 2024-2029 period. This demand shows how businesses are focused on deploying ERPs to manage all their business processes. ERP systems fall into two main deployment categories: Cloud-based and On-Premise setups.
Cloud-based ERP systems run on remote servers that users can access online. This setup has many upsides, like lower upfront costs, easy ways to grow, and providers taking care of updates. These ERPs also give users more freedom letting them log in from anywhere with the internet. These cloud options need less tech gear and maintenance from the business itself since providers handle most of the technical stuff.
On-premise ERP platforms run on the company’s hardware and servers. This traditional setup gives businesses complete control over their data and system changes. Companies with specific security needs or those in regulated industries often choose On-Premise ERPs. While they have higher initial costs and ongoing upkeep duties, they work without needing internet access. On-premise options also allow for more tailored solutions to meet unique business needs, but updates and upgrades can take longer and cost more than cloud options.
When we group ERP software based on how much you can change it, we see two main types: Off-the-Shelf and Custom ERP solutions.
Off-the-shelf ERP systems are pre-made software packages designed to meet common business needs across various industries. These products offer a standard set of features and functions that companies can put to use. Off-the-shelf ERPs cost less and take less time to set up than custom options. They get regular updates and improvements based on industry norms and what users say they need. However, they might not fit a company’s exact processes, which could mean the business has to change some of its practices to work with what the software can do.
Custom ERP solutions are built to meet the specific needs of individual companies. Developers create these systems from the ground up or modify existing platforms to fit an organization’s workflows, processes, and unique requirements. Custom ERPs offer the most flexibility and can be designed to work with current systems while meeting industry-specific needs. Although they provide an exact match for what an organization needs, custom solutions cost more upfront, take longer to develop and implement, and need ongoing upkeep. Companies with specialized processes or those working in niche industries where off-the-shelf solutions don’t cut it often choose custom ERPs.
ERP software solutions are grouped by business size needs split into two tiers:
Enterprise Scale ERP platforms are built for big companies that handle complex operations in many locations. These full solutions help manage complicated business processes across different departments. Key features include:
These ERP systems are made for small to medium-sized companies. They balance features and prices by focusing on core business tasks. Key features include:
Generic ERP platforms are built to meet the needs of many industries and business types. These systems offer a wide range of functions that work for different sectors. Key features include:
Industry-specific ERP systems, or vertical solutions, are built to meet unique sector needs. These platforms integrate deep industry knowledge, industry-specific features, and regulations. For example, the footwear industry ERP will have features like size management, defect analysis, and made-to-order management. In contrast, a textile ERP will have features for bales or lot-wise management.
The choice between Generic and Industry-specific ERP systems on a few key things. These include how complex industry processes are, what rules you need to follow, and whether you want ready-made features or the ability to customize. Generic ERPs can work in many business verticals. On the other hand, Industry-specific ERPs offer solutions custom-made for industries. They are more feature-rich and have better outcomes compared to off-the-shelf solutions.
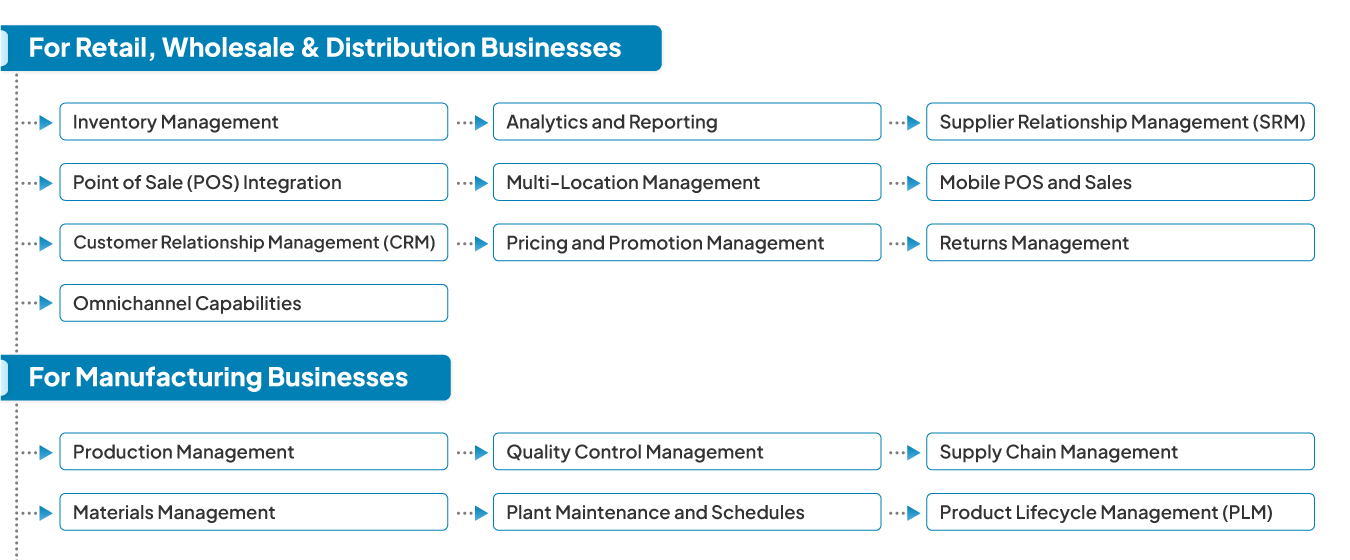
Custom-made ERP software has more features than off-the-shelf software. However, whatever you need to deploy, look out for the below key features:
ERP software for retail businesses has key inventory features. These include full stock management with item tracking, stock control, and transfer requests between locations. The system gives a current view of inventory levels across channels. This prevents running out of stock.
The built-in POS system makes checkout faster and updates inventory right away. It works with many payment types and handles transactions with discounts, loyalty point additions, and returns. This makes shopping easier for customers.
The CRM part helps monitor customer contacts, purchase actions, and what they’ve bought before. Deliver more personal marketing plans with the CRM feature of the ERP software. Also, you can create loyalty programs, offers and promotions, and membership plans with the ERP software.
Retail ERP software combines online and offline channels, including e-commerce platforms. Advanced ERP software also helps in create and run custom e-store. Businesses can manage their physical and online stores with the same ERP. This ensures prices, promotions, and stock stay the same across all channels, giving customers a smooth shopping experience.
The system provides in-depth reporting with different report types such as sales, stock, warehouse, billing, and customer relationships. Up-to-the-minute analytics help spot patterns, predict demand and further improve operations to boost profits.
ERP software allows businesses to manage multi store management from one place showing real-time stock, sales, and performance figures. The system handles stock transfers between stores. Businesses can also set location-specific pricing or keep pricing the same across all locations. Get combined reports to analyze the entire business.
Retail ERP systems have advanced pricing tools to implement strategies across channels. They support different pricing models, such as tiered and customer-specific pricing, and promotional campaign management. Quick and dynamic price changes (bulk price updates) help maintain a competitive edge.
The SRM module makes supplier interactions smoother through automated quote requests, order placement, and performance tracking. It helps businesses map their products to specific suppliers for faster procurement. It keeps an eye on delivery times and quality metrics letting companies make data-driven supply chain choices for better results.
Mobile Point of Sale features let staff process transactions anywhere using smart devices. Employees can see real-time inventory and customer data helping them make informed suggestions and finish sales on the spot. This tool supports billing for pop-up stores, retail stores, and kiosks at outdoor events.
The system handles returns using automated processes to refund and restock items. It keeps track of why products are returned to spot quality problems. The tools also update the returned item in real time.
Production management is at the heart of manufacturing ERP software. This feature makes production smoother from start to finish. It includes scheduling, planning capacity, and managing work orders. It makes production runs more efficient and gives managers a clear view of what’s happening in real-time, so they can make quick decisions. This part of the system works with inventory and quality control to keep operations running well.
ERP software offers full tools to manage materials, including buying and stock control. It keeps the right amount of raw materials in stock and orders supplies based on production plans. This makes sure there’s always enough while keeping costs down.
The quality control features help keep products at a high standard through checks, reports on problems, and fixes. The system keeps an eye on quality measurements and works with production parts to make sure quality rules, SOPs, and protocols are followed.
The software handles plant upkeep and machine schedules to stop shutdowns. It watches how equipment performs, looks after spare parts, and sends out maintenance alerts to keep production steady.
The system has supply chain management capabilities to predict demand and plan logistics. It makes the supply chain better from buying to delivery showing where goods are and helping work better with suppliers.
PLM tools handle a product’s whole life from design to disposal. This covers product development features, BOM control, and ways to manage engineering changes. The module speeds up development, cuts time to market, and lets all departments see up-to-date product info while keeping compliance records.
Apart from the above features of manufacturing ERP that are most popular, with custom ERP software, you can also get features like:

ERP software has an impact on lean management practices in manufacturing and retail sectors by making operations more efficient and cutting out waste. Take textile manufacturing as an example. Textile ERP systems can make fabric-cutting processes better to cut down on scraps. In food production, it can help to manage perishable stock more, which leads to less spoilage.
Retail businesses can use ERP to put just-in-time inventory practices into action, which cuts storage costs and boosts cash flow. By giving up-to-the-minute data on production processes, stock levels, and how resources are used, ERP allows businesses to spot and get rid of activities that don’t add value. This improves overall operational effectiveness and cuts costs. ERP helps in implementing and following lean manufacturing processes like Kaizen.
ERP systems give manufacturers and retailers data-driven insights to make smarter decisions. ERP analytics can predict changes in market demand helping manufacturers change production as needed. For instance, ERP for garment manufacturing can look at sales data to forecast fashion trends, rising design trends, etc.
Retail stores can use ERP-generated reports to improve store layouts, product placements, product assortments, and sales strategies based on how customers behave. By bringing together data from different departments and offering advanced analysis tools, ERP turns raw data into useful information. Using these analytics, managers can make quick and confident decisions.
ERP software has a big impact on boosting productivity in manufacturing and retail. For instance, the food and beverages manufacturing ERP can handle recipes. This keeps product quality steady and cuts down on human mistakes. ERP can plan production better. This means less machine downtime and more output.
In stores, ERP makes the whole process smoother, from when a customer orders to their checkouts. Advanced ERPs also have self-checkout features. It also cuts down on entering the same data twice and automates routine jobs.
ERP systems play a key role in making sure companies follow rules in both making and selling goods. Food and beverage manufacturers can use ERP to keep tabs on nutritional info in their products, handle info about things that might cause allergies, and create the documents needed for food safety rules like FSSAI. In the garment manufacturing business, ERP helps stick to laws about workers and the environment.
Stores can use ERP to follow laws that protect buyers, keep data private, and pay the right taxes. By automating compliance-related tasks, maintaining audit trails, and providing up-to-date regulatory information, ERP minimizes the risk of non-compliance, protects businesses from penalties, and builds trust with customers and regulatory bodies.
ERP systems are causing a revolution in supply chain management for manufacturers and retailers alike. The steel industry ERP provides full visibility from raw material sourcing to finished product shipping, which helps better teamwork with suppliers and shipping partners. ERP has an impact on fine-tuning stock levels based on sales predictions and how long products last. Retailers can use ERP to handle supply chains across many channels making sure items are in stock in physical stores and online shops. By offering live tracking, sales forecasting, and supplier performance stats, ERP helps manufacturers build resilient, quicker, and cheaper supply chains.
ERP software gives manufacturers and retailers a clear view of their business operations as they happen. In footwear manufacturing, ERP dashboards show current production numbers, stock levels, and how machines are running. This lets managers tackle stock-level challenges easily. Footwear ERP also offers up-to-date info on order status, how production is going in what quantity, and where shipments are.
Even retail stores with multiple branches and locations can see right away how sales are doing across different locations or online. Seeing things in real-time helps businesses make smart choices, fix issues faster, and serve customers better by giving everyone accurate current information.
ERP systems have a big impact on making products and services better in factories and stores. For instance, FMCG manufacturing units can use ERP to check quality at every step of production and distribution. FMCG ERP can help in quality testing procedures by providing pre-defined checklists to quality assurance engineers.
Retailers can use returns data obtained from ERP to determine product issues and reduce returns rates. ERP helps companies keep things top-notch, have fewer mistakes, and make customers happier.
ERP systems have a big impact on turnaround times in manufacturing and retail operations. ERP can make production scheduling better, which cuts down the time from when an order is placed to when it’s delivered. ERP can shorten product development cycles by improving teamwork between R&D, production, and marketing teams.
In retail, ERP can make checkout faster and help process online orders more. By automating workflows, getting rid of bottlenecks, and giving real-time information, ERP helps businesses respond faster to what customers want, reduce cycle times, and get ahead of competitors by being quicker and more efficient.
ERP systems help manufacturing and retail businesses take action before problems occur. In steel plants, ERP can predict when machines might break down by looking at how they’re working. This lets companies fix things before they break and costs a lot of money.
For food manufacturers, ERP can forecast demand spikes, enabling proactive production planning to meet increased demand. Retailers can use ERP to anticipate inventory shortages based on sales trends and automatically trigger reorders.
ERP software has a big impact on cutting down operational complexity in manufacturing and retail settings. For instance, textile manufacturers have complicated production lines. ERP can make it easier to handle various production steps. In the food industry, ERP can streamline recipe management and scaling, simplifying the handling of complex recipes.
Retailers can use ERP to run omnichannel operations bringing together in-store, online, and app-based sales channels. By offering a single platform for all business tasks setting standard processes, and providing easy-to-use interfaces, ERP makes day-to-day operations less complex.
In short, ERP systems contribute to top-line growth and bottom-line improvement across industries. Remember the benefits of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software are intrinsically tied to its quality and features. To select the best ERP for your business, assess your company’s requirements by focusing on and discussing your key workflow needs such as inventory control, production scheduling, sales monitoring, and more. Evaluate features, pricing structure, scalability, integration abilities, and ease of use specific to your industry. Give preference to software offering real-time data analytics and robust customer support. Review demos and customer feedback before finalizing the ERP.
If you need ERP software that can make a difference to your business and ease all your activities then, VasyERP should be your ERP software provider. VasyERP provides complete end-to-end ERP solutions for retailers, SMEs, MSMEs, wholesalers, distributors, enterprises, large chains, and manufacturing businesses.
For more details, schedule a demo now.

We all know that businesses are now working hard to tra...
July 11, 2023

Managing inventory and sales is a constant challenge fo...
December 6, 2024
